Kinematic Analysis of Wrist and Elbow Angles in Badminton Serve Techniques Based on IMU Sensors
Main Article Content
Perwita Aura Larasaty
Pringgo Widyo Laksono
Bambang Suhardi
Background: Motion capture technology is essential in sports biomechanics for analyzing human movement. Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) sensors offer a practical alternative to camera-based systems, providing real-time motion analysis. While previous studies in badminton biomechanics have largely focused on stroke phases or lower-limb movements using optical systems, few have investigated the detailed angular behavior of upper-limb joint-particularly the wrist and forearm during specific serve types. Moreover, existing research rarely compares different serve techniques in terms of kinematics using wearable IMU-based methods.
Aims: This study aims to analyze angular movement patterns of the wrist and forearm during different badminton serve techniques using IMU sensor. Understanding the wrist and forearm movements is crucial, as they directly affect shuttle control, serve conssitency, and injury risk- especiaally in high-spedd, repetitive motions like the badminton serve.
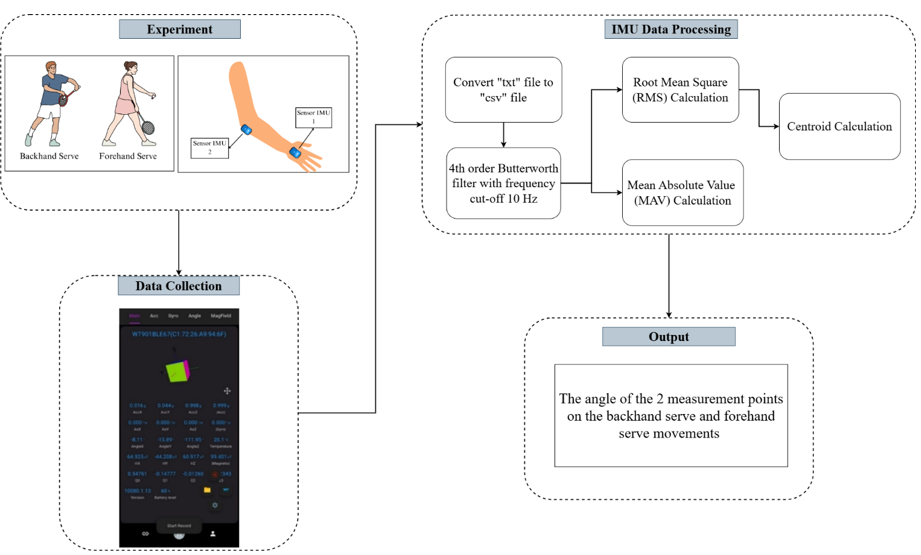
Methods: Sensors were placed on the dorsum of the hand and the forearm near elbow to measure angular motion in three serves: backhand, short forehand, and long forehand.
Result: Results indicate that the centroid calculation results showed that each type of serves had a different angular distribution pattern, with varying contributions from the forearm and wrist. The forearm plays a dominant role in generating power, while the wrist contributes more to directional control and stabilization. Results indicate that forearm movement is more dominant in forehand serves, while wrist movement is more pronounced in backhand serves. These findings suggest that IMU-based motion analysis can optimize badminton techniques, prevent injuries, and enhance training programs.
Aksan, H. (2012). Mahir Bulutangkis (1st ed.). Penerbit Nuansa Cendekia.
Aschenbrenner, P., Krawczyński, B., Krawczyński, M., Grzywacz, T., & Erdmann, W. (2023). Description of Telemark Skiing Technique Using Full Body Inertial Measurement Unit. Sensors, 23, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23073448
Association, W. M. (2013). Ethical Principles For Medical Research Involving Human Subjects.
Bastiaansen, B. J. C., Wilmes, E., Brink, M. S., de Ruiter, C. J., Savelsbergh, G. J. P., Steijlen, A., Jansen, K. M. B., van der Helm, F. C. T., Goedhart, E. A., van der Laan, D., Vegter, R. J. K., & Lemmink, K. A. P. M. (2020). An inertial measurement unit based method to estimate hip and knee joint kinematics in team sport athletes on the field. Journal of Visualized Experiments, 159, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.3791/60857
Brice, S. M., Phillips, E. J., Millett, E. L., Hunter, A., & Philippa, B. (2019). Comparing inertial measurement units and marker-based biomechanical models during dynamic rotation of the torso. European Journal of Sport Science, 767–775. https://doi.org/10.1080/17461391.2019.1666167
Espitia-Mora, L. A., Vélez-Guerrero, M. A., & Callejas-Cuervo, M. (2024). Development of a Low-Cost Markerless Optical Motion Capture System for Gait Analysis and Anthropometric Parameter Quantification. Sensors, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113371
Guignard, B., Ayad, O., Baillet, H., Mell, F., Simbaña Escobar, D., Boulanger, J., & Seifert, L. (2021). Validity, reliability and accuracy of inertial measurement units (IMUs) to measure angles: application in swimming. Sports Biomechanics, 1–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/14763141.2021.1945136
Hardwis, S., & Williyanto, S. (2023). Pengembangan Instrumen Tes Keterampilan Backhand Servis untuk Atlet Bulu Tangkis Usia Dini. Journal of Sport Coaching and Physical Education, 8(1), 16–27. https://journal.unnes.ac.id/sju/index.php/jscpehttps://journal.unnes.ac.id/sju/index.php/jscpe
Jacob, A., Nurshazwani, W., Zakaria, W., & Razali, M. (2016, September). Implementation of IMU Sensor for Elbow Movement Measurement of Badminton Players. 2016 2nd IEEE International Symposium on Robotics and Manufacturing Automation (ROMA).
Kuo, C., Liang, Z., Fan, Y., Blouin, J. S., & Pai, D. K. (2019). Creating impactful characters: Correcting human impact accelerations using high rate imus in dynamic activities. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 38(4), 47:1-47:12. https://doi.org/10.1145/3306346.3322978
Lee, Y. S., Ho, C. S., Shih, Y., Chang, S. Y., Róbert, F. J., & Shiang, T. Y. (2015). Assessment of walking, running, and jumping movement features by using the inertial measurement unit. Gait and Posture, 41, 877–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2015.03.007
Li, J., Zhu, K., Li, D., Kang, P., & Shull, P. B. (2024). 3D Knee and Hip Angle Estimation with Reduced Wearable IMUs via Transfer Learning during Yoga, Golf, Swimming, Badminton, and Dance. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 32, 325–338. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2024.3349639
Liu, M., Xin, P., Tang, Y., Shan, Y., Zhu, Z., Guo, Z., Zhou, L., Zhang, L., Liu, H., Huang, Y., & Li, B. (2025). Application of Inertial Measurement Units and Machine Learning for Fatigue Assessment in Badminton Athletes. Research Square, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-6204201/v1
Pedro, B., Cabral, S., & Veloso, A. P. (2021). Concurrent validity of an inertial measurement system in tennis forehand drive. Journal of Biomechanics, 121, 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2021.110410
Phinyomark, A., Phukpattaranont, P., & Limsakul, C. (2012). Feature reduction and selection for EMG signal classification. Expert Systems with Applications, 39(8), 7420–7431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2012.01.102
Purnama, S. K. (2010). Kepelatihan Bulu Tangkis Modern (1st ed.). Yuma Pustaka.
Rechy-Ramirez, E. J., & Hu, H. (2015). Bio-signal based control in assistive robots: a survey. Digital Communications and Networks, 1, 85–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcan.2015.02.004
Reuter, A. S., & Schindler, M. (2023). Motion Capture Systems and Their Use in Educational Research: Insights from a Systematic Literature Review. Education Sciences, 13, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13020167
Rusydi, M. I., Huda, S., Rusydi, F., Sucipto, M. H., & Sasaki, M. (2016). Pattern recognition of overhead forehand and backhand in badminton based on the sign of local Euler angle. Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, 2(3), 625–635. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijeecs.v2.i3.pp625-635
Rusydi, M. I., Sasaki, M., Sucipto, M. H., Zaini, & Windasari, N. (2015). Local Euler angle pattern recognition for smash and backhand in badminton based on arm position. 6th International Conference on Applied Human Factors and Ergonomics, 00, 1–6. www.sciencedirect.com
Shiang, T. Y., Hsieh, T. Y., Lee, Y. S., Wu, C. C., Yu, M. C., Mei, C. H., & Tai, I. H. (2016). Determine the Foot Strike Pattern Using Inertial Sensors. Journal of Sensors, 2016, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4759626
Tomita, Y., Iizuka, T., Irisawa, K., & Imura, S. (2021). Detection of movement events of long-track speed skating using wearable inertial sensors. Sensors, 21, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113649
Van Herbruggen, B., Fontaine, J., Simoen, J., De Mey, L., Peralta, D., Shahid, A., & De Poorter, E. (2024). Strategy analysis of badminton players using deep learning from IMU and UWB wearables. Internet of Things (Netherlands), 27, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iot.2024.101260
Wang, J., Liu, W., & Moffit, J. (2009). Steps for arm and trunk actions of overhead forehand stroke used in badminton games across skill levels. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 109, 177–186. https://doi.org/10.2466/PMS.109.1.177-186
Wardijono, B. A. (2013). Studi tentang Penangkap Gerakan (Motion Capture) Manusia. Jurnal Ilmiah Komputasi, 12(1), 1–6.
Windarto, A. P. (2017). Penerapan Data Mining Pada Ekspor Buah-Buahan Menurut Negara Tujuan Menggunakan K-Means Clustering. Techno.COM, 16(4), 348–357. https://www.bps.go.id.
Perwita Aura Larasaty , Sebelas Maret University, Indonesia
Department of Industrial Engineering, Sebelas Maret University, Surakarta, Indonesia
Pringgo Widyo Laksono , Sebelas Maret University, Indonesia
Department of Industrial Engineering, Sebelas Maret University, Surakarta, Indonesia
Bambang Suhardi , Sebelas Maret University, Indonesia
Department of Industrial Engineering, Sebelas Maret University, Surakarta, Indonesia