Sub-Watershed Prioritization for Sustainable Sediment Management in the Upper Cisokan Hydropower Catchment Using SWAT+
Main Article Content
Laella Pusparinda
Mariana Marselina
Background: Sedimentation poses a critical threat to hydropower sustainability, particularly in pumped storage systems such as the Upper Cisokan Pumped Storage (UCPS) plant in West Java, Indonesia.
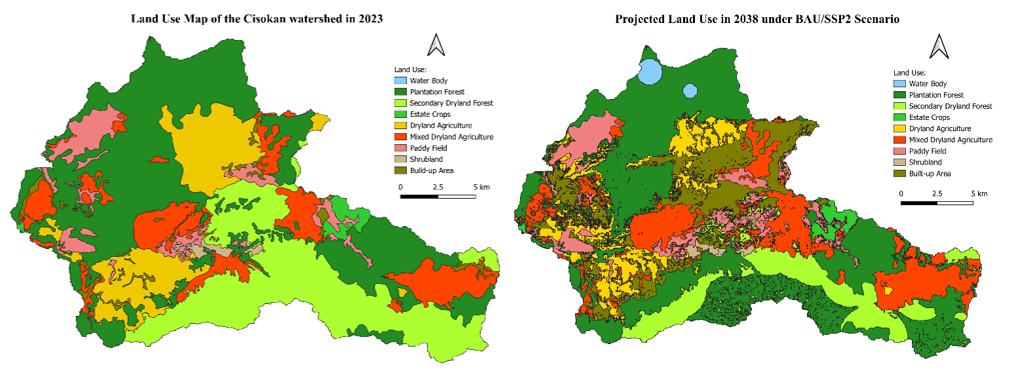
Aims and Methods: This study assesses the spatio-temporal dynamics of sediment yield in the Cisokan Watershed using the SWAT+ model, incorporating historical simulations (2013 and 2023) and a 2038 projection under a Business-As-Usual (BAU) scenario developed through supervised classification in Google Earth Engine (GEE).
Result: Model calibration based on observed discharge data yielded satisfactory results (NSE = 0.80 in 2013, 0.65 in 2023), validating its suitability for sediment analysis. Results reveal a nearly fourfold increase in average sediment yield from 0.61 to 2.25 tons/ha/year between 2013 and 2023, with a projected rise to 5.57 tons/ha/year by 2038. A composite prioritization index, integrating current sediment output, decadal change, and sub-watershed area, identified SW-23, SW-16, and SW-5 as the highest priority areas for erosion mitigation. These findings were validated against future projections, confirming their persistent erosion risk. The study emphasizes the importance of scenario-based watershed planning in safeguarding hydropower infrastructure. By integrating sediment modeling with scenario-based land use projection via supervised classification in Google Earth Engine (GEE), this study provides a replicable framework for proactive watershed management and hydropower sustainability planning.
Berhanu, A. B., Abera, W., & Demissie, T. (2020). Prioritization of sub watersheds to sediment yield and evaluation of best management practices: A case study of Finchaa catchment, Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Land, 10(6), 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10060650
Furqani, F., Syafri, Y. P., Octavia, D. M., Zayu, W. P., & Yunas, B. (2024). Rainfall-Runoff Transformation Analysis Using The HBV-96 Model in The Cidanau Watershed, Banten. Open Science and Technology, 4(2), 63–75. https://doi.org/10.33292/ost.v4i2.130
Gorelick, N., Hancher, M., Dixon, M., Ilyushchenko, S., Thau, D., & Moore, R. (2017). Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sensing of Environment, 202, 18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2017.06.031
Gupta, H. V., Kling, H., Yilmaz, K. K., & Martinez, G. F. (2009). Decomposition of the mean squared error and NSE performance criteria: Implications for improving hydrological modelling. Journal of Hydrology, 377(1–2), 80–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.08.003
Halder, S., RoyChowdhury, A., Kar, S., Ray, D., & Bhandari, G. (2024). Critical watershed prioritization through multi criteria decision making techniques and GIS integration for watershed management. Sustainability, 16(8), 3467. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16083467
López Pérez, A., Colín García, G., Moya, H., Bolaños González, M. A., Fernández-Reynoso, D. S., & Cruz Ramírez, A. S. (2024). Application of the Analytic Network Process for Sub Watershed Prioritization in the Huehuetán River Basin, Chiapas, Mexico. Land, 13(11), 1868. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13111868
Megersa, K. B., Demissie, T. A., & Koriche, S. A. (2020). Impacts of land use land cover change on sediment yield and stream flow: A case of Finchaa hydropower reservoir, Ethiopia. International Journal of Science and Technology, 6(4).
Moriasi, D. N., Arnold, J. G., Van Liew, M. W., Bingner, R. L., Harmel, R. D., & Veith, T. L. (2007). Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Transactions of the ASABE, 50(3), 885–900. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.23153
Noon, A. A., & Kim, M.-H. (2021). Sediment and cavitation erosion in Francis turbines—Review of latest experimental and numerical techniques. Energies, 14(6), 1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14061516
Noora, H., Bagherian Kalata, A., & Dastranja, A. (2022). Spatial prioritization of sediment source areas at watershed scale. Water Harvesting Research, 5(1), 40–52.
O’Neill, B. C., Kriegler, E., Ebi, K. L., Kemp-Benedict, E., Riahi, K., Rothman, D. S., ... & Solecki, W. (2017). The roads ahead: Narratives for shared socioeconomic pathways describing world futures in the 21st century. Global Environmental Change, 42, 169–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2015.01.004
Pande, C. B., Kundu, S., & Moharir, K. (2024). Characterizing land use/land cover change dynamics by an enhanced random forest machine learning model: a Google Earth Engine implementation. Environmental Sciences Europe, 36, 84. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-024-00901-0
Pontes, A. E., Coutinho, H. L. C., Mello, C. R., Beskow, S., & Oliveira, L. T. (2021). Assessing sediment yield and streamflow with SWAT model in a small sub-basin of the Cantareira system. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 45, e0200140. https://doi.org/10.36783/18069657rbcs20200140
Pusparinda, L., & Marselina, M. (2025). Land use change analysis on sediment yield in the Cisokan Watershed using SWAT+: Implications for the operation of the Upper Cisokan Pumped Storage Hydropower Plant. IGSC 2025 Proceedings. (accepted).
Riahi, K., van Vuuren, D. P., Kriegler, E., Edmonds, J., O’Neill, B. C., Fujimori, S., ... & Tavoni, M. (2017). The Shared Socioeconomic Pathways and their energy, land use, and greenhouse gas emissions implications: An overview. Global Environmental Change, 42, 153–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2016.05.009
Rodriguez, L. G., McCallum, A., Kent, D., Rathnayaka, C., & Fairweather, H. (2023). A review of sedimentation rates in freshwater reservoirs: recent changes and causative factors. Aquatic Sciences, 85(60). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-023-00960-0
Sadhwani, K., Eldho, T. I., Jha, M. K., & Karmakar, S. (2022). Effects of dynamic land use/land cover change on flow and sediment yield in a monsoon‑dominated tropical watershed. Water, 14(22), 3666. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223666
Serrão, E. A. O., et al. (2021). Impacts of land use and land cover changes on hydrological processes and sediment yield determined using the SWAT model. International Journal of Sediment Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsrc.2021.04.002
Sheeba, S., et al. (2023). Accuracy assessment of land use/land cover classification using machine learning classifiers in Google Earth Engine: A case study of Jammu District. Frontiers in Earth Science, 11, 1188093. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2023.1188093
Shrestha, R., & Shrestha, R. (2019). Impact of reservoir sedimentation on hydroelectric power generation: Case study of Kulekhani First Hydropower Station. IOE Graduate Conference, 7, 1–8.
Wang, Y., Yu, M., Zhang, W., Liu, D., & Xie, H. (2023). Land use and climate change impacts on hydrology and sediment yield in a typical subtropical watershed. Journal of Environmental Management, 326, 116746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116746
Yuan, L., & Forshay, K. J. (2020). Using SWAT to evaluate streamflow and lake sediment loading in the Xinjiang River Basin with limited data. Water, 12(1), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010039